Definition & Overview
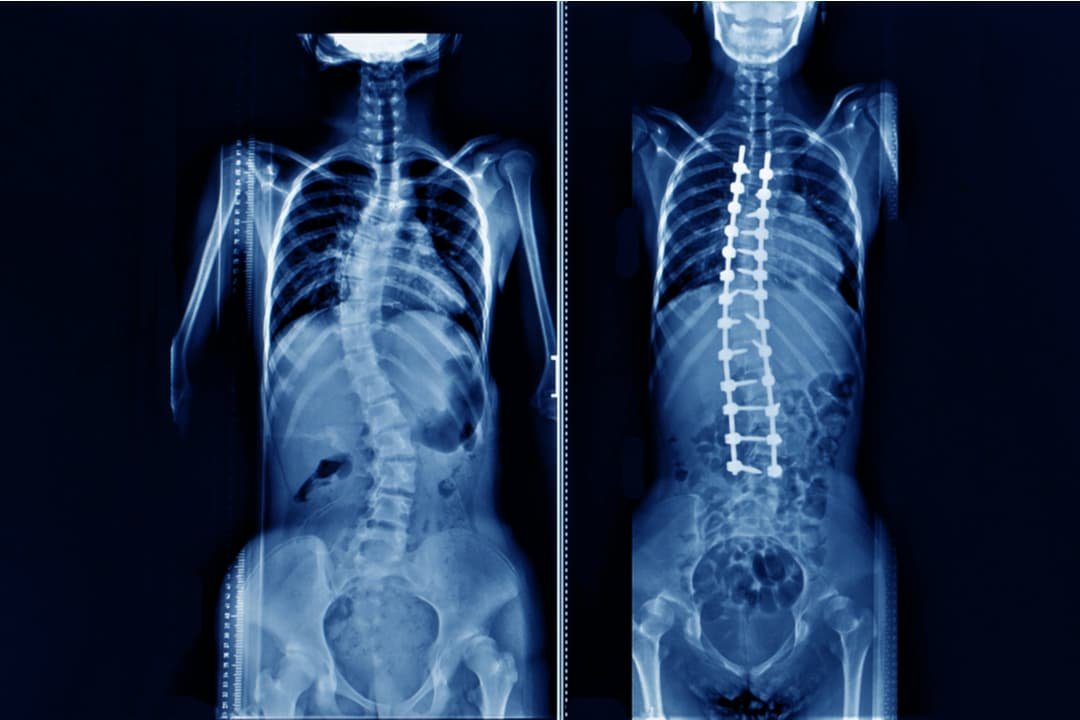
Scoliosis is an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine. It is most often diagnosed in childhood or early adolescence.
Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some spine deformities continue to get more severe as children grow. Severe scoliosis can be disabling. An especially severe spinal curve can reduce the amount of space within the chest, making it difficult for the lungs to function properly.
 [Image of normal vs scoliosis spine anatomy]
[Image of normal vs scoliosis spine anatomy]
Symptoms & Signs
There are several signs that may indicate the possibility of scoliosis. Parents should look for:
- Sideways curvature of the spine (S or C shape)
- Uneven shoulders (one blade sticks out more)
- Uneven waist or hips
- Sideways body posture
- Decreasing pulmonary function (in severe progressive cases)
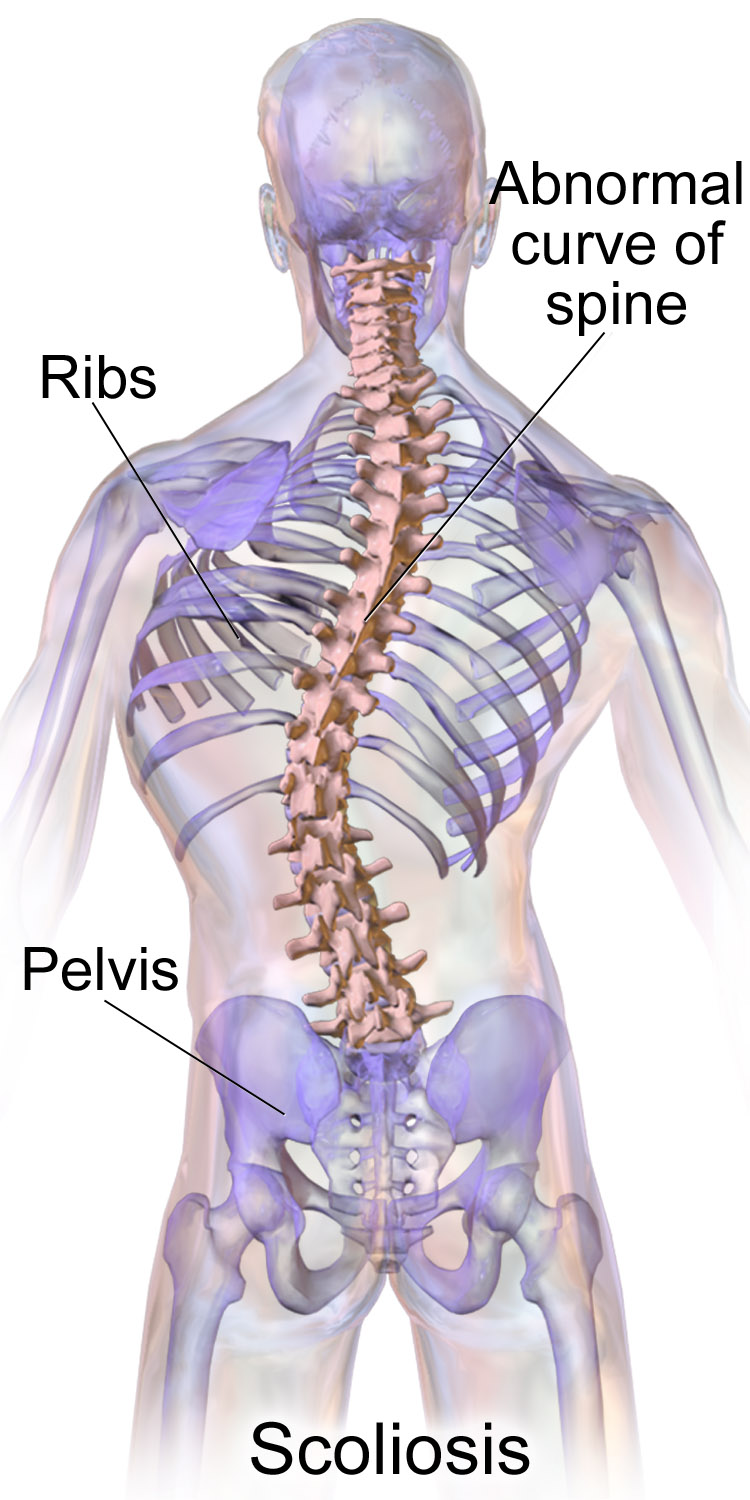
Causes & Risk Factors
Scoliosis shows up most often during growth spurts, usually between ages 10 and 15. About the same number of boys and girls are diagnosed with minor idiopathic scoliosis, but curves in girls are 10 times more likely to get worse and require treatment.
Possible causes include:
- Birth defects: Affecting an infant’s spinal bones (e.g., spina bifida).
- Injuries: Spinal injuries or infections.
- Neuromuscular conditions: Such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
Treatment Options
For mild scoliosis, you may not need treatment. Your doctor might watch you and take X-rays periodically to check for progression. Some children grow out of mild curves.
Braces
In kids who are still growing, wearing a brace around the torso can stop the curve from getting worse. They are usually made of plastic and often worn 24 hours a day. Modern braces are often invisible under clothes.
[Image of scoliosis brace types]Spinal Fusion Surgery
In this operation, pieces of bone or similar material are placed between vertebrae. Hardware (rods and screws) holds the bones in place until they fuse together. This straightens the spine and prevents worsening.
Exercise Program for Scoliosis
- Begin on hands and knees, back level.
- Inhale and arch your back (Cat).
- Exhale, drop the belly, and lift head toward ceiling (Camel).
- Do two sets of 10.

- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent.
- Reach overhead, grab right wrist with left hand.
- Bend slightly to the right to feel a stretch on the left side.
- Hold for 1-2 breaths, return to center.
- Repeat on opposite side. Do 5–10 reps.
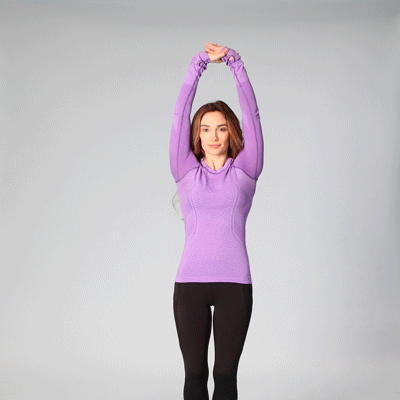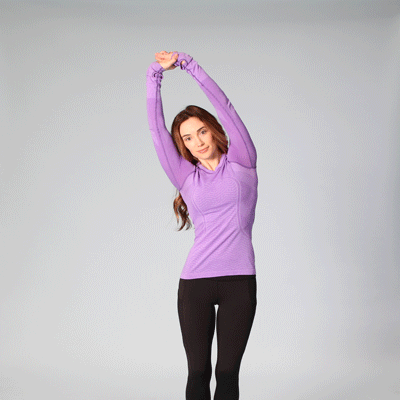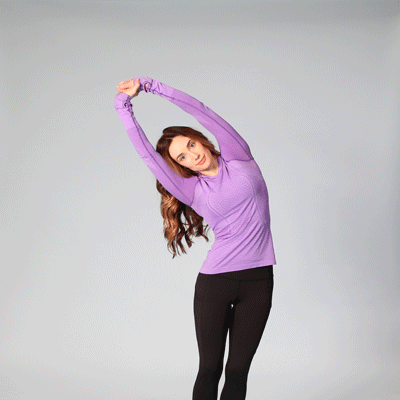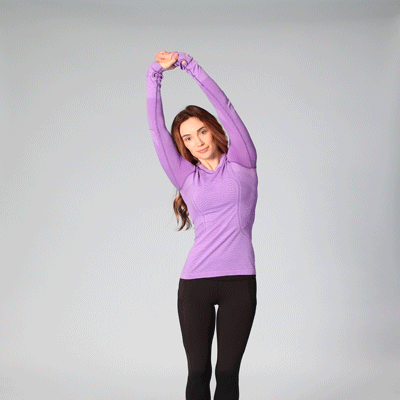
- Lie on your back with feet flat on the floor.
- Exhale and contract abs, pushing belly button toward floor to flatten back.
- Hold position for 5 seconds.
- Repeat 10 times.
